Creating a natural and sustainable pond environment can be an enriching journey, especially when you incorporate edible aquatic plants. These plants not only serve as beautiful additions to your landscape but also effectively filter pond water and support ecological health. In this guide, you will learn how to harness the power of edible aquatic plants like watercress, water lilies, pickerelweed, and aquatic mint to improve your pond’s water quality while enjoying their nutritional benefits.
Discovering the Power of Edible Aquatic Plants
Edible aquatic plants are essential to maintaining a healthy pond ecosystem. They absorb nutrients, sediments, and pollutants from the water, leading to improved water quality. These plants are more than merely functional; they enhance the aesthetic appeal of your pond, providing beauty, shade, and habitat for various wildlife.
By integrating edible plants into your pond, you can achieve a dual benefit: a visually pleasing environment and a robust aquatic ecosystem. Unlike traditional landscaping, these plants flourish in water and contribute to a self-sustaining habitat. Research indicates that many edible aquatic plants can absorb heavy metals and other contaminants, making them valuable allies in creating a healthier pond. Additionally, they often have higher protein and mineral content than conventional vegetables, which can be a nutritional bonus.
Colorful pond filled with a variety of edible aquatic plants (Source: Premier Pond)
Choosing the Right Edible Aquatic Plants for Your Pond
Selecting the right edible aquatic plants is crucial for maximizing the benefits to both your pond and your diet. Here are some excellent options:
-
Watercress: Known for its high levels of vitamins A and C, iron, and calcium, watercress is one of the most nutrient-dense greens available. It thrives in flowing water, which helps keep it healthy and vibrant.
-
Water Lilies: Besides their stunning blooms, water lilies produce seeds rich in protein and nutrients. They not only beautify your pond but also contribute to its ecological balance.
-
Pickerelweed: This plant produces edible seeds and tender stalks, while its young leaves can be enjoyed as greens. Its presence improves biodiversity and water quality.
-
Aquatic Mint: This fragrant plant adds culinary value to your dishes while enriching the pond environment with its aromatic qualities.
Research shows these edible aquatic plants often outperform traditional vegetables in nutritional content, thereby enhancing your pond’s ecological health and providing additional food sources.
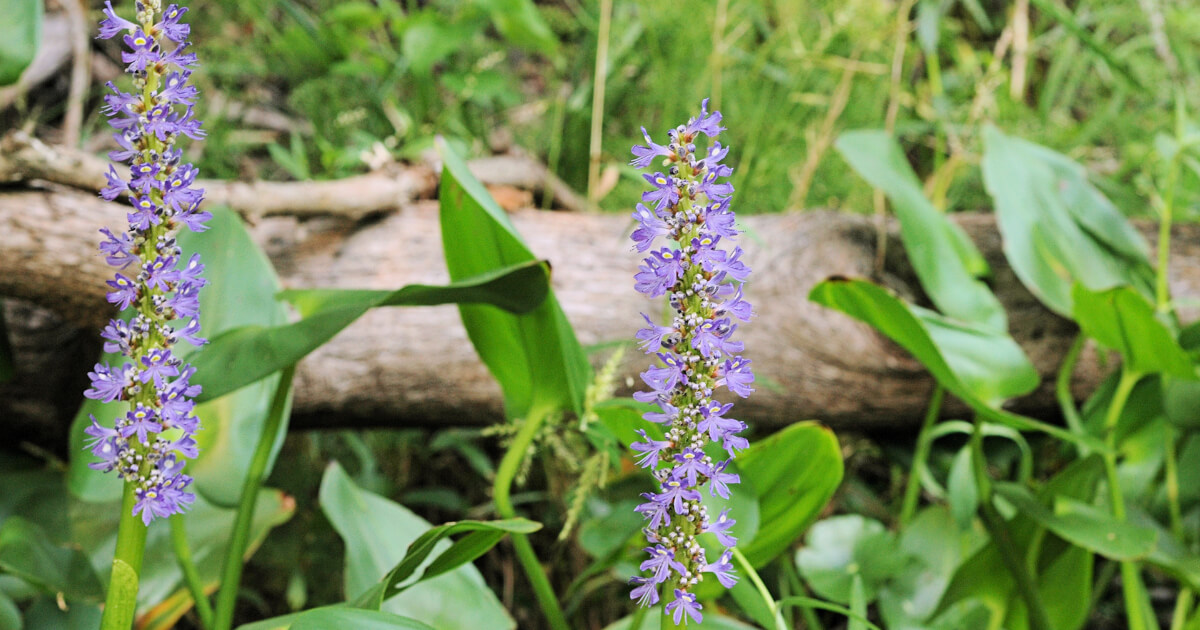

Close-up of Pickerelweed, an edible aquatic plant (Source: University of Florida)

Image of fragrant white water lilies (Source: NH Garden Solutions)
Integrating Aquaculture and Permaculture: A Sustainable Approach
To make the most of your edible aquatic plants, consider combining aquaculture and permaculture practices. Aquaculture focuses on raising fish, while permaculture is about sustainable land use design. Together, they create a self-sustaining environment that benefits both your pond ecosystem and your food production.
In such systems, fish waste provides nourishment for the plants, while the plants filter and purify the water in return. This natural cycle minimizes maintenance needs and enhances nutrient absorption, leading to better water quality.
To successfully implement this strategy, you should monitor water circulation and nutrient levels, ensuring a balanced ecosystem. Numerous case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of aquaponics systems where edible aquatic plants significantly improve water conditions and provide food.

Diagram illustrating connections between aquaculture and permaculture systems (Source: TreeYo Permaculture)
The Art of Sustainable Pond Maintenance
Maintaining a sustainable pond requires regular monitoring of plant health and water quality. Creating a schedule for these assessments is vital to ensure a thriving ecosystem.
Here are some best practices for harvesting edible aquatic plants:
-
Harvest Timing: Aim for late spring when plants are young and packed with nutrients.
-
Proper Tools: Use appropriate tools such as hand-held nets or rakes to collect the plants carefully.
-
Complete Removal: Attempt to remove the entire plant, including its roots, to prevent regrowth and fragmentation.
Monitoring water quality is equally important, and regular testing for pH, nutrients, and contaminants will help you maintain a safe and productive pond. Avoid over-harvesting to preserve the ecological balance and enhance the health of your ecosystem.
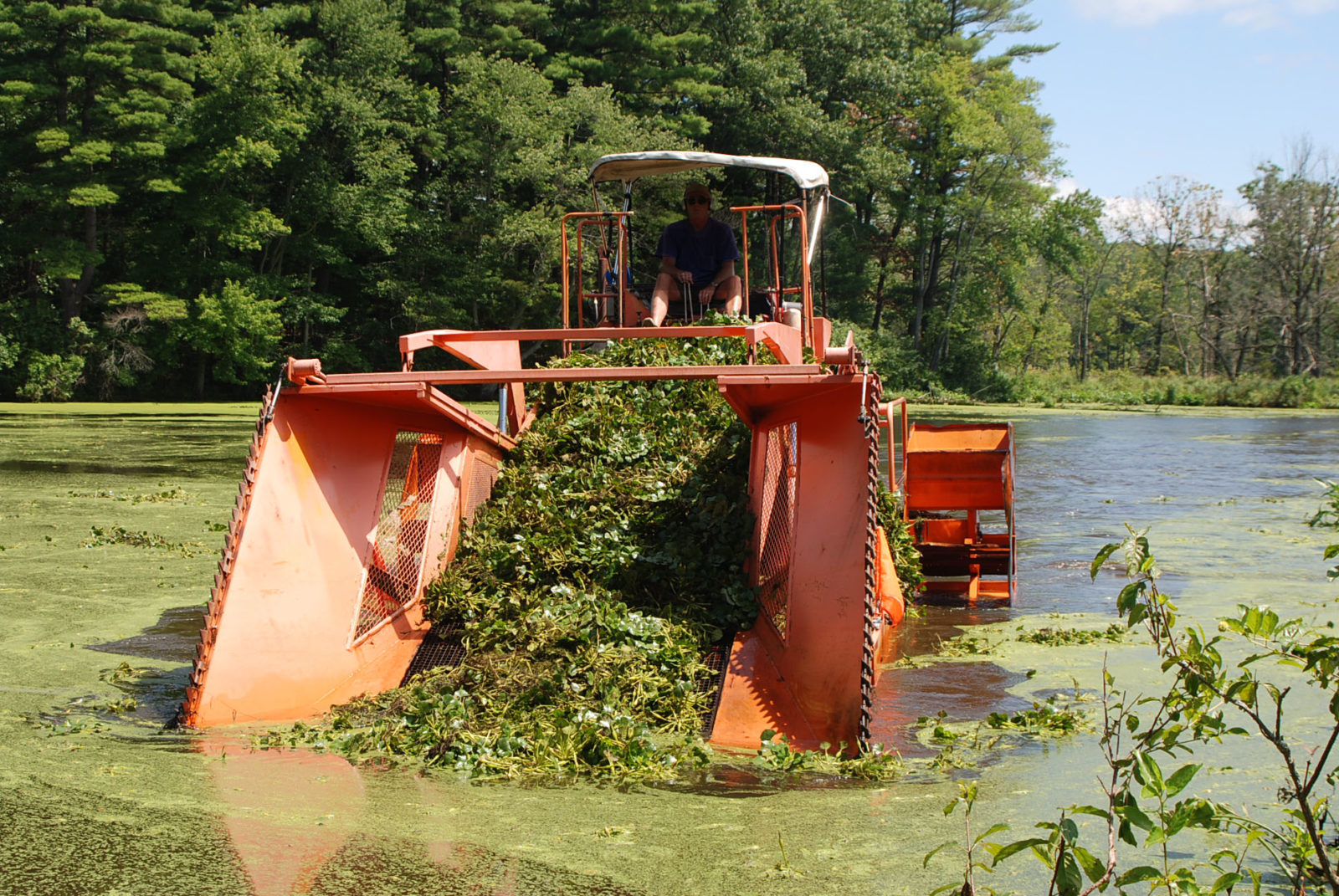

Image showing mechanical harvesting methods for aquatic plants (Source: Solitude Lake Management)
Evaluating Cost Benefits of Edible Aquatic Filtration
Using edible aquatic plants for pond filtration can lead to significant cost savings over time. While initial investments may include planting and establishing these edible plants, the long-term benefits often outweigh these costs.
For many homeowners, adopting natural filtration through edible plants reduces expenditures associated with traditional filtration systems. These plants not only purify water but also provide an additional food source, contributing to cost-effectiveness. Research has demonstrated that incorporating edible plants lowers the operational costs of aquaculture while enhancing water quality and crop yield.
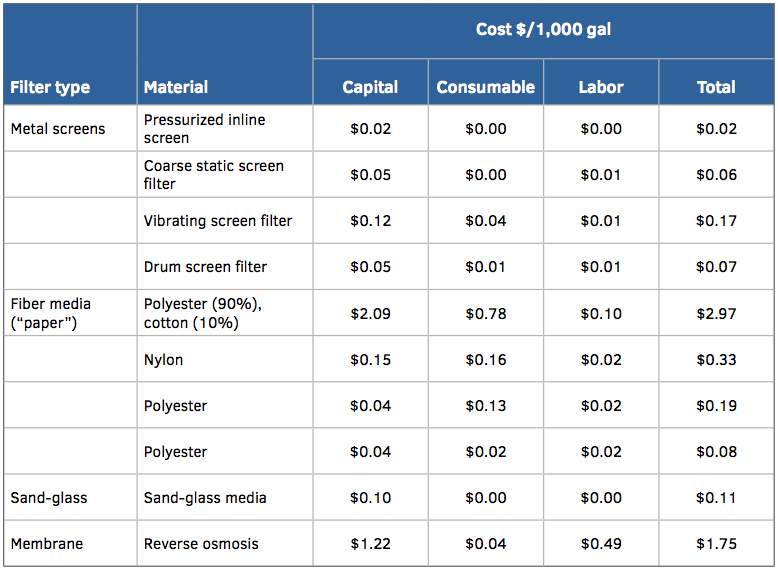
Table graph comparing the costs associated with various filtration methods (Source: Greenhouse Product News)
Enhancing Your Pond’s Ecosystem Naturally
The addition of edible aquatic plants enriches your pond’s ecosystem by attracting beneficial wildlife. These plants can provide habitats and sustenance for various species, including birds and beneficial insects.
To promote biodiversity, select plants known to attract specific wildlife. For example, flowers from certain aquatic plants can lure pollinators, while others offer shelter for fish and amphibians. Together, these elements work to foster a balanced ecosystem, leading to a healthier pond environment.
The integration of natural filtration and diverse habitats leads to improved water clarity and reduced harmful algal blooms. By absorbing excess nutrients from the water, these plants help maintain the pond’s ecological integrity.
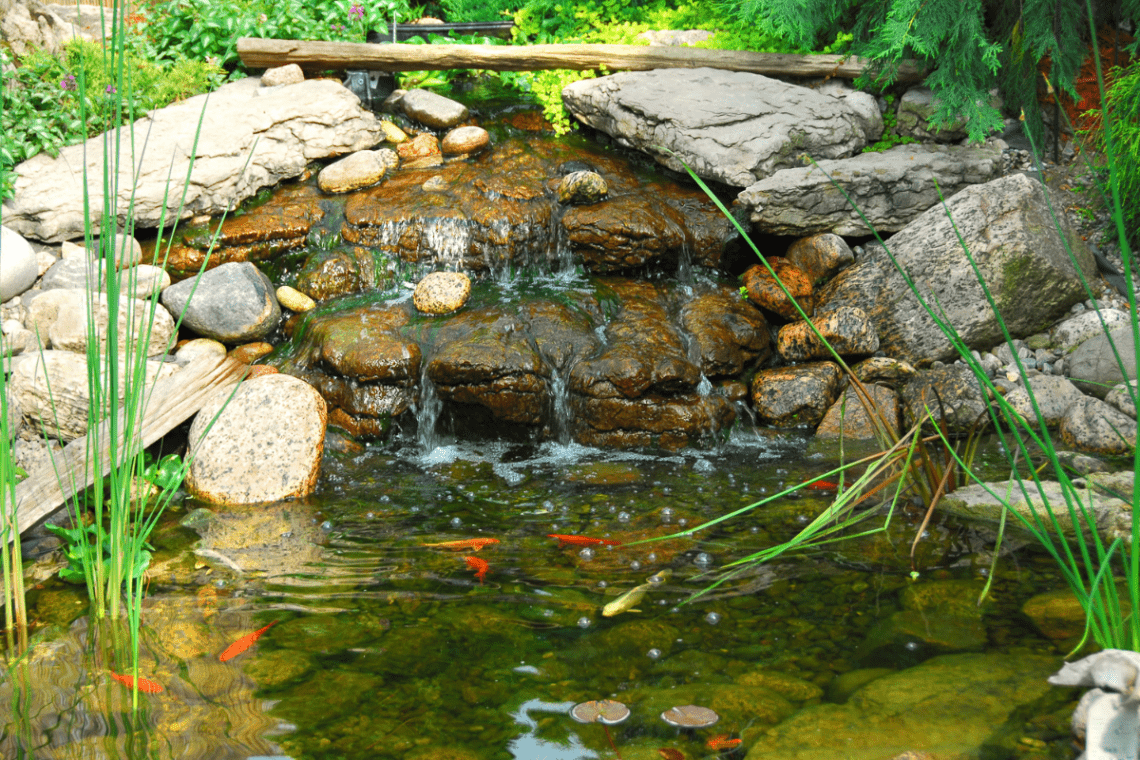

Illustration showing interactions within a pond ecosystem involving aquatic plants and wildlife (Source: Pond and Garden Design)
Safety and Precautions: Enjoying Edible Aquatic Plants
While harvesting and consuming edible aquatic plants can enhance your diet, safety must come first. Proper identification of edible versus toxic plants is crucial for avoiding health risks.
Quality testing of pond water is essential to ensure safety. Make sure to check for pollutants, such as heavy metals or harmful nutrients, before consuming any plants. Always wash harvested plants thoroughly to remove contaminants and adhere to proper cooking methods.
Familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding the harvesting of aquatic plants to ensure compliance, particularly in public water bodies.

Infographic summarizing safety tips for harvesting and consuming aquatic plants (Source: Iowa State University)
Real-life Success Stories of Edible Aquatic Plants in Pond Filtration
Several real-life examples highlight the benefits of implementing edible aquatic plants in pond filtration. Home gardens and community projects have experienced positive outcomes, including enhanced water quality and nutrient availability.
In aquaponics systems, these plants have consistently demonstrated significant improvements in water conditions while providing fresh produce. Whether in large-scale operations or small residential settings, these successes showcase how adaptable and beneficial edible aquatic plants can be.
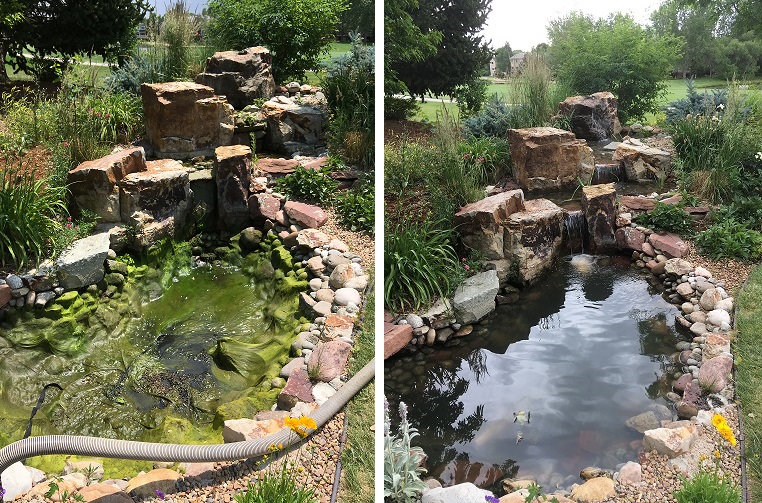

Before and after images demonstrating the effectiveness of pond cleanout and plant introduction (Source: Colorado Pond Pros)
Conclusion
Harnessing edible aquatic plants for sustainable pond filtration offers a wealth of benefits for both your garden and the environment. By selecting the right plants, implementing sustainable practices, and monitoring your pond’s health, you can foster a thriving ecosystem that supports both your landscape and lifestyle.
As you incorporate these plants into your pond system, appreciate the balance between functionality and beauty. You’re creating a harmonious environment that not only serves your gardening needs but also enhances the ecosystem around you for years to come.

