Unveiling the Wonders of Exotic Fish in Your Pond
Keeping exotic fish in swimming ponds offers both aesthetic appeal and the enhancement of biodiversity, creating a lively aquatic environment. Exotic fish significantly transform a pond, adding vivid colors and dynamic movements that captivate observers. Additionally, the presence of various species contributes to a balanced ecosystem, promoting healthier water conditions and reducing potential pest populations.
Swimming zones are essential for the well-being of both fish and humans. These zones are classified into three primary areas: the surface, mid-water, and bottom zones. Each zone accommodates different fish species and serves distinct functions, with the surface zone providing light and air, the mid-water zone as a transitional space, and the bottom zone serving as habitat for scavengers and detritivores. Understanding these zones allows pond owners to create a harmonious environment where fish can thrive alongside swimmers while maintaining water quality and visual appeal.
Successfully creating a system where exotic fish coexist with swimmers requires careful planning, a focus on water quality, and thoughtful fish selection. The choice of exotic fish plays a significant role in improving pond aesthetics, enhancing biodiversity, and sustaining ecological stability. By harmonizing various species suitable for each swimming zone, pond owners can create not only an appealing retreat but also a thriving ecosystem.
An engaging image of a swimming pond featuring vibrant fish swimming at different levels, illustrating the beauty and diversity of aquatic life (Source: Fontana Water Features)
Choosing the Right Fish for the Surface Swimming Zone
Surface swimming zones are vital for maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems. In this area, fish thrive while utilizing the available light and air, creating a robust and captivating environment. Exotic fish suitable for surface zones include Hatchetfish, Gouramis, Halfbeaks, Guppies, and Angelfish. These species are known for their peaceful behavior and compatibility with one another.
-
Hatchetfish (Carnegiella species): Known for their remarkable jumping abilities, these small fish typically measure around 2-3 inches, making them well-suited for surface dwelling.
-
Gouramis (Trichopodus species): These colorful fish breathe air through their labyrinth organ. They are best kept in groups and thrive among floating plants, offering shelter and comfort.
-
Guppies (Poecilia reticulata): Hardy and adaptable, guppies can easily coexist in community tanks while adding vibrant colors and lively behavior.
Ideally, surface zones should contain approximately 20-25% of the total fish population. An optimal ratio for surface dwellers is 1-2 fish per 5 gallons of water, ensuring adequate space for thriving without competition from mid or bottom-dwelling species.
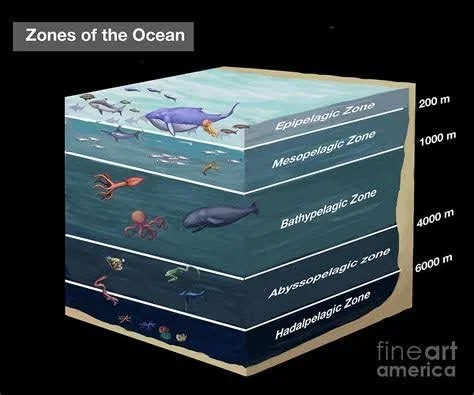
A diagram illustrating different aquatic zones, ideal for explaining surface zones and the types of fish suitable for these areas (Source: Squarespace)
Navigating the Mid-Water Wonders: Fish Choices and Ratios
Mid-water zones are essential for maintaining ecological balance and providing a habitat for various fish species. This area typically hosts schooling fish, such as Tetras, Rasboras, and Barbs. The mid-water zone occupies the largest portion of the tank, ideally comprising around 50-60% of the total fish population. A useful guideline is to allocate one inch of adult fish length per gallon of water to ensure ample swimming space.
Species chosen for the mid-water zone include:
-
Neon Tetra (Paracheirodon innesi): This vibrant fish is easily recognized by its blue and red stripe, demonstrating excellent schooling behavior that enhances community dynamics.
-
Rasboras: Known for their social nature, these fish thrive in groups and contribute to the tank’s liveliness.
By creating a balanced population structure, the mid-water zone supports the overall vitality of the tank. Maintaining optimal ratios and promoting schooling behavior helps enhance the stability of the aquatic ecosystem, allowing fish to exhibit natural behaviors with minimal stress.

An illustrative diagram showing the division of aquatic zones based on depth, visually representing mid-water living fish species (Source: iStock)
Creating an Inviting Bottom Zone: Choosing the Right Fish
Bottom zones play an integral role in an ecological habitat as they host essential scavengers and detritivores, including species such as Catfish, Loaches, and Corydoras. These fish are crucial for maintaining cleanliness by consuming organic waste and leftover food. Bottom-dwelling fish typically make up about 20-25% of the total fish population in a pond, ensuring they effectively fulfill their ecological roles.
Optimal stocking ratios specify one bottom-dwelling fish per 10-15 gallons of water, preventing overcrowding while maintaining ecological balance. Specific recommendations for bottom-dwelling fish include:
-
Corydoras Catfish (Corydoras species): With their peaceful demeanor, these small catfish contribute to the health of the aquarium while benefiting from a tank enriched with plants and hiding spots.
-
Loaches: Active and curious, these fish add dynamic movement to the bottom zone and engage in social behavior when kept in groups.
Creating an inviting bottom zone involves providing ample hiding spots and substrate variation. This enhances the comfort of bottom-dwelling fish and promotes their health and well-being within the community.

This image depicts a natural aquatic landscape showcasing bottom-dwelling fish, emphasizing the importance of habitat features for these species (Source: Oregon Conservation Strategy)
The Art of Compatibility: Ensuring Different Zones Harmonize
Compatibility issues often arise when mixing fish from different swimming zones, creating potential conflicts in shared habitats. Common concerns include territorial disputes, feeding competition, and stress levels among active and sedentary species. Understanding these challenges is crucial for promoting harmonious cohabitation.
To mitigate conflicts:
-
Create Distinct Territories: Utilize aquascaping with rocks, logs, and plants to define and separate various segments of the aquarium, thereby facilitating a sense of security for all species.
-
Use Effective Feeding Strategies: Provide a mix of food types suitable for different species to ensure all fish receive adequate nutrition, thus minimizing competition.
For example, territorial fish can exhibit aggressive behaviors towards schooling species when space is not adequately defined. Maintaining a balanced ratio of active and less active fish ensures that territorial behavior does not adversely affect tank dynamics. Overall, diligent planning promotes peaceful coexistence among diverse species.

A compatibility chart that visually represents which fish species can coexist across different swimming zones in a pond (Source: Aquarium Industries)
Maintaining Water Quality: The Backbone of a Healthy Ecosystem
Water quality and filtration systems are vital for keeping a multi-zone aquarium healthy. Different areas of the pond may require tailored filtration approaches to address the specific needs of the fish inhabiting those zones. This includes mechanical, biological, and chemical filtration systems.
Essential practices for optimal water quality include:
- Specific Filtration Needs: Each zone should have its dedicated filtration setup to manage waste and improve water clarity. For instance:
- Surface Zone: Requires skimmers to remove surface debris.
- Mid-Water Zone: Needs biological filters to handle ammonia and suspended particles.
- Bottom Zone: May benefit from undergravel filters to prevent detritus buildup.
Incorporating these filtration strategies into the overall design allows pond owners to maintain a clean and healthy environment for diverse fish populations.

An infographic showcasing filtration systems tailored for different pond zones, essential for evaluating water quality and ecology management (Source: Pinterest)
Natural Techniques for Reducing Algae and Enhancing Fish Health
Effective management of algae growth is a common concern among pond owners. Utilizing natural methods can mitigate algae proliferation while simultaneously maintaining fish health. Integrated approaches rely on both the presence of aquatic plants and specific fish species to create a balanced ecosystem.
Strategies for natural algae control include:
- Utilizing Floating Plants: These plants limit sunlight penetration, inhibiting algae growth by absorbing excess nutrients from the water.
- Choosing Compatible Fish Species: Incorporating algae-eating species, such as certain types of catfish, can help maintain a healthier balance.
Ultimately, cultivating an environment where natural processes can flourish leads to enhanced ecological stability, benefitting the overall health of the aquatic habitat.

Before-and-after images demonstrating the effectiveness of natural algae control methods, highlighting the role of fish in maintaining water quality (Source: Naturalake)
Wrapping It Up: Crafting a Thriving Ecosystem for All
In conclusion, harmonizing exotic fish with swimming zones requires careful selection of species, vigilant maintenance of water quality, and creating an aesthetically pleasing environment. By understanding the specific needs of different fish types and their respective zones, pond owners can cultivate an ecosystem that thrives and provides a tranquil haven for both fish and humans.
Key strategies for building a balanced ecosystem include:
- Regular monitoring of water parameters and fish behavior.
- Thoughtful selection of compatible species that enhance biodiversity.
- Incorporation of aquatic plants for both aesthetic appeal and functional contributions.
By adhering to these guidelines, pond owners can establish a lasting environment that successfully integrates the beauty of exotic fish with the joy of swimming, ultimately creating a thriving ecosystem for years to come.
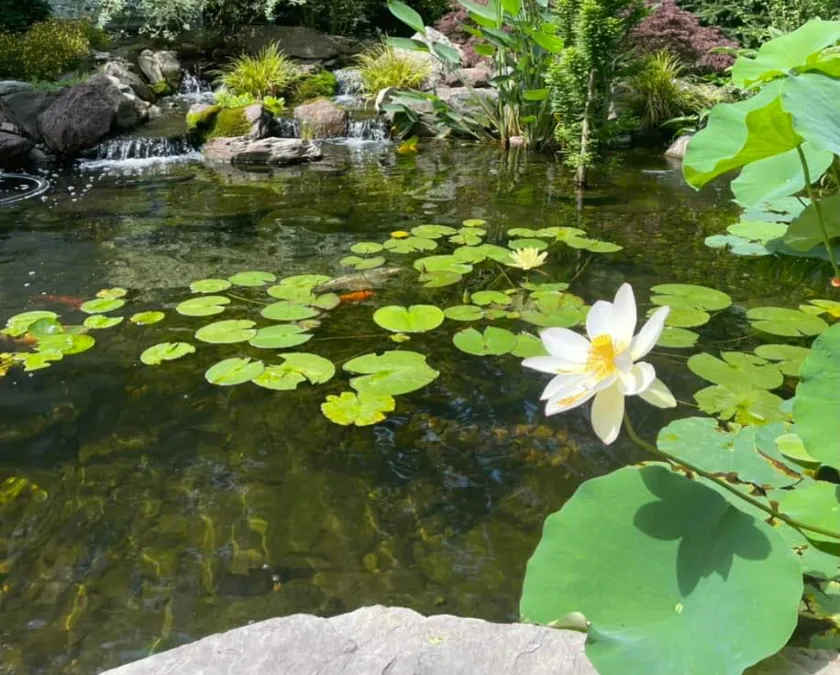

A vibrant and flourishing ecosystem pond, showcasing aquatic plants and healthy fish populations, providing a perfect conclusion visual (Source: Charlotte Backyard Ponds)

