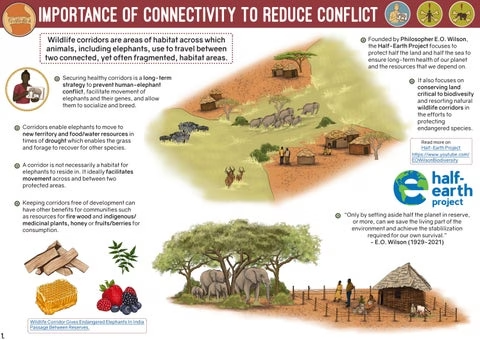
Why Connecting Wildlife Habitats Matters
Wildlife connectivity refers to the ability of animals to move freely between different habitats, which is vital for maintaining biodiversity. This movement is essential for species to access resources, evade threats, and reproduce successfully. However, wildlife habitats are increasingly threatened by urbanization, climate change, and infrastructure development. As natural landscapes become fragmented, animal populations can become isolated, which often leads to reduced genetic diversity and diminished overall health of species.
Research indicates that enhancing connectivity can lead to significant improvements in wildlife populations. For instance, a study conducted in the Carpathian Mountains documented a 78% increase in large mammal crossings following the installation of wildlife corridors[1]. Additionally, prairie corridors in North America have shown to increase genetic diversity among butterfly populations by 30%[3].
These findings highlight the critical importance of implementing connectivity measures such as wildlife corridors and stepping stones. These strategies not only support biodiversity but also strengthen ecosystems by facilitating natural processes essential for ecological health.
An infographic depicting the effects of habitat changes due to fragmentation (Source: ISU Publication)
Exploring Effective Wildlife Connectivity Strategies
Various strategies have been developed to enhance wildlife connectivity across different ecosystems. Wildlife corridors, which are natural or artificial strips of land that allow animals to navigate between fragmented habitats, have proven to be effective. Often designed with fencing to direct animal movement, these corridors help maintain habitat integrity. For example, wildlife overpasses in Montana have been shown to reduce vehicle collisions by 80%, underscoring the effectiveness of such designs in facilitating safe crossings[16].
Stepping stones, or small patches of habitat strategically placed between larger areas, are another important connectivity measure. Research from Florida has demonstrated that stepping stones can increase amphibian movement by 62% between isolated wetlands[2].
Urban planners are also beginning to incorporate habitat networks into city landscapes, integrating green spaces and wildlife corridors to enhance connectivity. This shift illustrates that tailored solutions can address the specific needs of diverse ecosystems, ultimately benefiting overall biodiversity.

A depiction of various wildlife corridors designed for improving habitat connectivity (Source: USDA Forest Service)
Harnessing Technology for Better Connectivity
Recent advancements in technology have become instrumental in assessing and improving habitat connectivity. Remote sensing is one of the most promising approaches. A 2024 study introduced the LINK methodology, which employs remote sensing data to evaluate functional landscape connectivity. This method utilizes movement data to generate visual assessments of habitat networks, aiding conservation planning[1].
Drones are also increasingly used in conservation efforts. In Northern Ireland, drones are effectively employed to map vegetation types and monitor habitat conditions, enabling more precise assessments of connectivity[3]. Furthermore, machine learning integrated with satellite imagery creates detailed ecological maps that highlight connectivity barriers and opportunities.
Genetic analysis has emerged as a vital tool in connectivity research. By examining genetic flow between populations, scientists can identify essential habitats for protection. These technologies enhance the capability to implement effective connectivity measures and ensure that conservation efforts are informed by accurate, data-driven insights.
An image illustrating remote sensing technology in habitat mapping (Source: MDPI Remote Sensing)
Navigating Legal Landscapes for Habitat Connectivity
Legal and policy frameworks have a profound impact on habitat connectivity initiatives worldwide. In the United States, new legislation has improved opportunities for wildlife connectivity. The Wildlife Crossings Pilot Program, part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, has successfully enhanced state-level connectivity by providing funding for wildlife crossing projects[5].
In contrast, the European Union offers strong legal frameworks aimed at enhancing habitat connectivity. The EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 seeks to develop a cohesive Trans-European Nature Network, emphasizing biodiversity preservation across member states[3].
However, challenges persist due to fragmented governance. Coordination challenges among federal and state agencies can hamper the effective implementation of connectivity measures. Strong private property rights in countries like the U.S. often complicate the establishment of wildlife corridors on non-public lands[5].
As the demand for effective habitat connectivity grows, it is crucial that legal frameworks adapt to support these critical conservation initiatives.
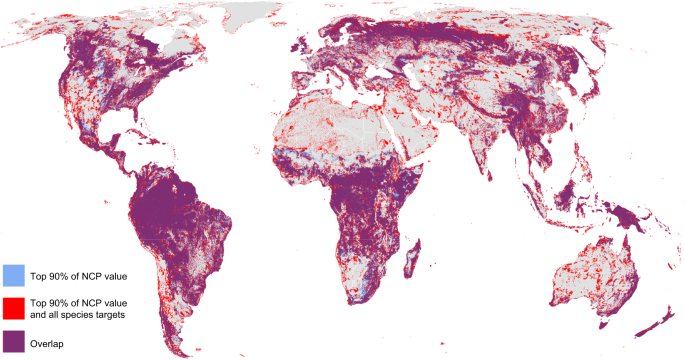
A world map illustrating legal frameworks supporting biodiversity (Source: Nature Communications)
Economic Insights on Habitat Connectivity Projects
The economic implications of implementing habitat connectivity projects are significant. Cost-benefit analyses consistently demonstrate substantial economic advantages associated with these initiatives. A 2025 study by Scioto Analysis indicated that a well-placed wildlife crossing could yield approximately $14 million over its lifetime by reducing accidents and enhancing ecosystem services[8].
Wildlife crossings have been shown to reduce wildlife-vehicle collisions by up to 97%[11]. These projects also stimulate local economies by creating jobs in construction, engineering, and environmental assessment.
Funding sources for habitat connectivity are increasingly varied, with federal initiatives such as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act providing essential financial backing for conservation efforts[9]. As funding becomes more accessible, there is greater potential for implementing wildlife connectivity projects that yield both ecological and economic benefits.
Graphs depicting financial analyses related to habitat connectivity projects (Source: MDPI Land)
Learning from Successful Global Connectivity Projects
Numerous successful large-scale connectivity projects worldwide offer valuable lessons for future initiatives. The Yellowstone to Yukon (Y2Y) Conservation Initiative exemplifies a long-term strategy for connecting habitats across vast regions, with over 500,000 acres of land protected through collaborative efforts[19].
The European Green Belt, which follows the former Iron Curtain, has successfully executed more than 150 conservation projects while engaging local communities by highlighting its historical significance[1].
Successful initiatives emphasize the importance of adaptivity and multi-stakeholder collaboration. Integrating economic considerations into conservation strategies helps cultivate local support and ensures sustainability for connectivity efforts. Analyzing successful case studies allows planners to derive actionable insights that inform future connectivity initiatives.
A before-and-after visual showcasing habitat restoration efforts (Source: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service)
Getting Involved: How Communities Can Support Local Biodiversity
Active participation in local biodiversity initiatives can significantly impact wildlife connectivity. Grassroots movements play an essential role in raising awareness and advocating for conservation efforts. Community members can engage in habitat restoration projects, such as planting native vegetation and managing invasive species.
Building partnerships with local governments and nonprofit organizations is vital for creating effective conservation networks. Participating in discussions with stakeholders can help establish connectivity measures that align with community values and needs.
Furthermore, identifying funding opportunities for local projects enhances efforts to promote biodiversity and connectivity. Organizations such as the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation offer various grant opportunities aimed at advancing habitat conservation initiatives[15]. By participating in local biodiversity projects, communities can contribute meaningfully to the preservation of natural ecosystems.

A visual checklist individuals can use to support biodiversity in their communities (Source: Honestly Modern)
Conclusion
Connecting wildlife habitats is a vital strategy for enhancing biodiversity and ensuring ecosystems remain resilient. Effective wildlife corridors, stepping stones, and innovative technologies all contribute to facilitating wildlife movement in increasingly fragmented landscapes.
Legal frameworks play an essential role in supporting these initiatives; however, challenges persist in harmonizing governance with private interests. Economic evaluations illustrate the feasibility of connectivity projects, highlighting their potential to yield substantial community benefits.
By learning from successful global projects and adopting actionable strategies at the local level, communities can play a critical role in advancing wildlife connectivity. Through collaborative efforts, informed planning, and active engagement, the preservation of biodiversity and the enhancement of connectivity in natural habitats can be effectively achieved.